Trauma-Related Disorders: Diagnosis and Treatment in Therapy
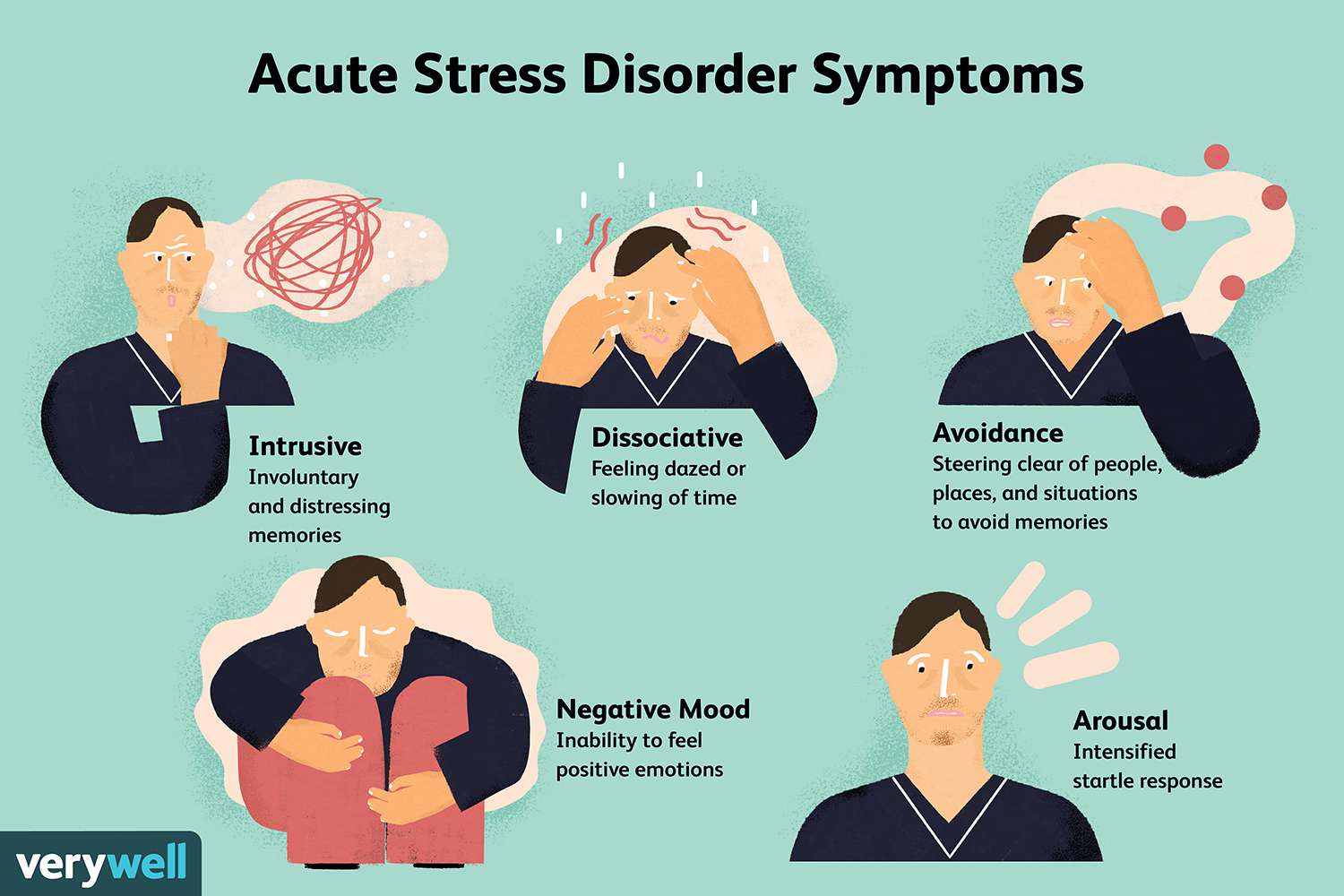
Trauma-related disorders are a group of psychological conditions that can develop as a result of experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. These disorders include post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), acute stress disorder (ASD), dissociative disorders, and adjustment disorders. Diagnosing and treating trauma-related disorders requires a comprehensive understanding of the complex effects trauma can have on individuals.
Diagnosis of trauma-related disorders begins with a thorough assessment of the individual’s symptoms, history, and experiences. Clinicians use diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) to determine if the individual meets the criteria for a specific disorder. Symptoms such as intrusive thoughts, nightmares, avoidance behaviors, hyperarousal, and changes in mood and cognition are carefully evaluated to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Once a trauma-related disorder is diagnosed, appropriate treatment options can be explored. The primary goal of therapy is to help individuals process the traumatic event, reduce distressing symptoms, and improve overall functioning. Here are some commonly used treatment approaches:
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely recognized and effective treatment for trauma-related disorders. With this, Calgary CBT therapy provides specialized and compassionate care, utilizing the principles of cognitive behavioral therapy to help individuals overcome negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping strategies. It involves identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs related to the trauma https://cedarwaytherapy.com/grief-counselling-toronto . CBT also incorporates techniques such as exposure therapy, where individuals are gradually exposed to traumatic memories or situations in a safe and controlled manner, helping to reduce avoidance behaviors and reestablish a sense of safety.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a specialized therapy approach specifically designed for trauma treatment. It involves guiding individuals to visually track bilateral eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation while focusing on traumatic memories. EMDR facilitates the reprocessing of traumatic experiences, helping individuals to desensitize and integrate these memories, leading to symptom reduction and healing.
Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT): TF-CBT is a specialized form of CBT designed specifically for children and adolescents who have experienced trauma. It combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with trauma-focused interventions to address the unique needs of young individuals. TF-CBT involves psychoeducation, skill-building, and trauma processing to support recovery.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT is a therapeutic approach originally developed for individuals with borderline personality disorder but has been found to be effective for trauma-related disorders as well. DBT focuses on teaching individuals skills to manage emotions, improve distress tolerance, and enhance interpersonal effectiveness.
Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage specific symptoms associated with trauma-related disorders, such as anxiety, depression, or sleep disturbances. Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications are commonly used, but their use should be carefully evaluated by a psychiatrist or prescribing physician.
It is important to note that therapy for trauma-related disorders should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs, preferences, and cultural background. Therapists should create a safe and supportive environment where individuals feel heard and validated. Collaboration between therapist and client is essential in establishing treatment goals and selecting appropriate interventions.





